Growth Hormone Deficiency In Children
Growth hormone deficiency or DHC is a rare childhood disorder. It is caused by a low production of this substance by the pituitary gland, located at the posterior base of the brain.
It can be caused by a brain injury, the presence of a tumor or having received some type of radiation to the head. There are also other diseases that are capable of producing DHC.
This pathology is not hereditary. In many cases, the cause of this condition is unknown, there are even children who suffer from it from birth. Likewise, a relationship of this deficit with congenital deformations has been seen, as could be the case of cleft lip and cleft palate.
The deficiency of this hormone could be related to the insufficient presence of other hormones , such as corticotropin, gonadotropins, thyrotropins and avsopressin. These hormones regulate important biological processes.
The continuous pediatric medical control allows detecting the deficiency in growth hormone early to take the appropriate clinical measures. Parents or guardians of the child should be aware of the alarm signals. In this way, they will have an accurate diagnosis to promptly address this abnormality.
Possible signs of DHC in children
The most obvious sign of suspected CHD is a child’s short stature compared to others of the same chronological age. The slow growth is noticeable in the size of the face and extremities, as well as in a body, which appears more robust.
Similarly, poor muscle development and a very small penis are observed in men. Glucose is deficient in the blood and puberty is delayed.
On the other hand, it is also necessary to observe the self-esteem of the child, who could feel physically different from his peers and, therefore, more vulnerable.

Diagnosis of growth hormone deficiency
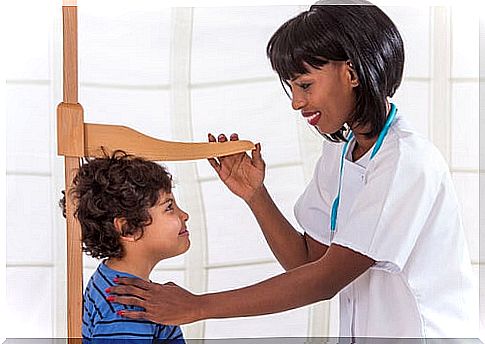
Periodic medical check-ups include monitoring the child’s growth curve on a comparison chart. It is in this type of analysis when a deficiency in this regard can be detected.
One of the first tests done on the child, when in doubt, is an X-ray of the hand. Its development is capable of revealing bone age and body growth rate. Another study that allows determining the bone age of the person is dual-energy radioabsorciometry.
Most likely, the doctor will order a blood test to find out at what level the IGF or insulin growth factor type 1 is.
One way to detect the disorder is to provoke the generation of growth hormone with drugs that stimulate the pituitary gland. Once administered, the body response is evaluated.
Other endocrine tests include determining the production of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (HLG).
Finally, an MRI of the brain can be done. With this, the aim is to evaluate the normality of the gland that produces the hormone or the presence of some other pathology causing the disorder.
Clinical treatment of growth hormone deficiency
The treatment to address the growth deficit caused by hormones consists of the prescription of a drug. It is a synthetic version of the hormone that is given by subcutaneous injections. The doctor will determine the dose, frequency and duration of the medication. Such treatment could last into adulthood.
With the DHC, the child grows less than five centimeters or two inches annually. However, with proper treatment, it can grow 25 centimeters or 10 inches in a year. This is a great result when compared to the side effects that may occur, which are usually mild to moderate.

Some of those effects are:
- Breast augmentation in men.
- Scoliosis.
- Muscle and joint pain.
- Inflammation of upper and lower limbs (hands and feet).
- Headache
- Mild hypothyroidism
Rarer and less common are serious side effects, such as headache with impaired vision, pancreatitis, or hip bone problems.
Prompt diagnosis is what will ensure that treatment for growth hormone deficiency produces the desired results. In this way, those who suffer from it can achieve optimal body development and normal height in adulthood.